Choosing an ERP system: 7 considerations for companies
Other
January 30, 2026
Choosing an ERP system is one of the most important decisions a company can make, as it directly affects efficiency and competitiveness. Below are seven key considerations to help you make the right decision:
Clarification of business needs: Analysis of specific operational goals and processes.
Industry-specific features: The benefits of solutions tailored to the needs of a particular sector.
Technical infrastructure: Compatibility of the existing IT system and growth opportunities.
Supplier rating: A reliable partner who supports the company in the long term.
Features and customization: Flexibility of basic features and customization options.
Financial considerations: Managing costs, returns, and hidden expenses.
User experience: Employee involvement and acceptance of the system.
These considerations will help ensure that the chosen ERP system supports the company's operations and growth in the long term.
The Ideal ERP: 7 Steps to Strategic Selection and Implementation for SMEs
https://youtu.be/L5i6fOcx7C0
1. Business needs and objectives
Before selecting an ERP system, it is important to accurately determine the company's current situation and long-term goals. This forms the basis for subsequent detailed analyses. According to research by KPMG Hungary, many companies are unable to take advantage of automation opportunities because they do not clarify in advance what they expect from the new system.
The first step is to conduct a business process reengineering (BPR) analysis to help identify gaps in existing software and operational issues. It is worth examining whether inventory management, financial integration, or administrative process automation require improvement. Requirements can be divided into two main categories: functional (such as industry-specific tasks) and non-functional (such as system architecture, IT security, or integration options). These basic considerations will help you evaluate additional criteria for your ERP system.
In order to make an objective decision, it is worth weighting the criteria. In addition, prepare a business plan that includes net present value (NPV), cost-benefit analysis, and return on investment (ROI) calculations. Research shows that applying enterprise architecture (EA) methodology before selecting an ERP system can reduce system complexity by up to 30% and result in a 10% increase in efficiency per workstation.
Another key factor is scalability. The ERP system must be able to handle growing user, transaction, and functional demands. Modular systems are particularly advantageous because they allow you to activate only those functions (such as CRM, project management, or IoT) that you currently need.
"The choice of ERP system has a decisive impact on the future operation and profitability of a company." - Bálint Molnár, Eötvös Loránd University
2. Industry-specific functions
General ERP systems offer basic functions, but industry-specific solutions come with pre-built workflows tailored to the needs of a particular sector. This makes these systems not only faster to implement, but also more cost-effective, as they require less customization.
Every industry faces its own unique challenges and expectations. For example:
Retail: Omnichannel sales, POS integration, and loyalty card management are of paramount importance.
Construction industry: Subcontractor management and resource planning are essential requirements.
Manufacturing: Production management, MRP, and real-time monitoring play a critical role.
Logistics: Tracking expiration dates and courier service integrations (e.g., GLS, Foxpost) are essential.
Padraig Murphy, ERP & CPM Account Manager, sums up the advantages of industry-specific systems as follows:
"Industry-specific ERP solutions come with pre-built features designed for the workflows and business processes of that particular industry. This means you can start using the solution right away and enjoy the benefits immediately." - Padraig Murphy
Legal compliance is also a fundamental consideration. For companies operating in Hungary, it is essential that the ERP system supports NAV data synchronization, automatic VAT reporting, and complies with Hungarian accounting and tax regulations.
Choosing a supplier with industry experience is also crucial. It is worth choosing a partner who not only offers technological solutions, but also provides specialized consultants (such as production engineers or logistics experts) and has a thorough understanding of the challenges of the sector.
3. Technical infrastructure and growth capacity
The long-term success of ERP systems is fundamentally influenced not only by industry specifics, but also by technical infrastructure. Before choosing a new ERP system, it is worth considering carefully whether the existing IT environment is capable of supporting the new system or whether infrastructure upgrades will be necessary. System architecture, IT security, and integration capabilities are all key factors in ensuring that ERP fits seamlessly into the existing environment.
Modern cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly popular because they eliminate internal maintenance requirements and offer flexible scalability. On-premise systems are now considered obsolete, which is why most service providers offer a subscription (OpEx) model similar to how Netflix-like services operate.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) technology allows ERP systems to be easily connected to other existing and future applications, avoiding complex, custom coding solutions. For example, Australian fuel retailer Ampol used an iPaaS platform in 2024 to accelerate its integration projects by 70% while achieving a 30% cost reduction.
Another advantage of the modular system structure is that the company can start with the basic functions and then gradually expand the system with special modules, such as production management, IoT, or CRM functions, as business needs grow. The central database ensures data consistency and real-time analysis even with higher data traffic.
When planning for the long term, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) over a 10-year period, including the cost of future upgrades. With outdated architectures, for example, all programming changes must be redone during a version change, which can significantly increase operating costs.
These technical and financial considerations form the basis for further evaluation of ERP systems.
4. Supplier evaluation and support services
The successful implementation of an ERP system depends not only on technical considerations, but also on the partner—i.e., supplier—we choose for the process.
The quality of the supplier plays a fundamental role in the success of ERP implementation. Research shows that the suitability of the software, the quality of the information, and the services provided by the supplier together determine the success of the project. A poorly chosen supplier can not only prolong the implementation time, but also increase resource requirements and costs.
Financial stability and market position are also key factors. A supplier with a stable financial background can ensure long-term updates and support. It is therefore worth thoroughly examining the supplier's financial situation, competitiveness, and business environment. Industry references and credible case studies help you understand how the system performs in practice. This information forms the basis for a detailed financial and support analysis, which is essential for continuous operation.
The implementation of an ERP system does not end with technical implementation. The quality of support services directly affects the long-term stability of the system. Service Level Agreements (SLAs), for example, guarantee that system errors will be handled within a specified time frame, ensuring "smooth and uninterrupted use." It is important that the supplier has sufficient experts, especially during the go-live and holiday periods, as these can be critical moments. A lack of expert consultants is responsible for 15% of ERP implementation failures.
Reliable suppliers not only support the company during installation, but also contribute to long-term cooperation through continuous product development and regular technical and legal updates. When demoing, it is worth avoiding pre-prepared presentations and instead requesting a demonstration based on the company's specific scenario.
5. Features and customization options
Once we have determined the technical basis of the ERP system and the growth opportunities, it is worth reviewing the functions and customization options in detail.
A thorough understanding of the basic functions of an ERP system is essential for making the right choice. A well-functioning ERP must be based on a central database where data is recorded once and is immediately available to all departments. The most important modules include financial management (e.g., automated invoicing and real-time cash flow monitoring), inventory management (real-time inventory level control, automatic reorder notifications), and procurement and logistics (supplier contract management, approval processes).
Due to the specific requirements of the Hungarian market, the system must include local functions such as NAV data synchronization, compliance with Hungarian invoicing rules, and support for local tax regulations. These functions are closely related to the technical and industry requirements discussed earlier.
Striking a balance between customization and basic functionality is key. Configurable settings that can be adapted to specific needs help avoid deeper code modifications. This not only reduces implementation risks and costs, but also makes the system more flexible. Modular solutions allow a company to start with basic functions (such as invoicing and inventory management) and then expand the system later with specialized modules such as IoT integration or social media marketing. This approach ensures that the system evolves as the company grows.
"ERP implementation is only possible if the organization has the capacity to change." – Travis Anderegg
Before starting customization, it is worth reviewing business processes thoroughly to avoid automating old, potentially inefficient practices in the new system. Successful customization can bring practical benefits. When evaluating vendors, it is worth requesting a demo that is specifically tailored to your company's unique needs and processes, rather than a generic presentation.
6. Financial investment and return
The costs of an ERP system can be divided into two main categories: one-time investments (such as license fees and infrastructure) and ongoing operating costs. The chosen installation method has a significant impact on costs. Cloud-based solutions typically start at $2,400/month/user, while on-premises implementations require a higher one-time investment. In addition, potential hidden costs should not be overlooked, as they can have a significant impact on the final expenditure.
To cover such hidden costs—such as data migration, reduced work pace, or process rethinking—it is worth planning for a 10–20% reserve in the budget.
"The return on ERP investment is about linking the impact of the system to specific business results and then quantifying those improvements in a way that makes sense in the company's income statement." – Dmytro Umen, CEO and co-founder of Brights
To accurately calculate the return on investment, you must first determine the total cost of ownership (TCO). This includes both direct costs (such as software and hardware costs) and indirect costs (such as training, downtime, and lost productivity). ROI is calculated using the following formula: (Net profit / Total investment) × 100. To calculate the payback period, divide the initial investment by the annual net cash flow.
When evaluating return on investment, it is important to consider not only tangible benefits (such as reduced labor costs or lower inventory costs), but also less measurable benefits. These include, for example, improved customer satisfaction and more accurate decision-making.
Switching to a cloud-based ERP system can reduce TCO by up to 30% by eliminating the need for hardware investments and internal IT support. In Hungary, special attention must be paid to the integration of modules that comply with local tax and invoicing rules. These not only help avoid fines, but can also reduce the costs of manual corrections. All of these elements contribute to the ERP system truly delivering business success.
7. User experience and implementation planning
Even the most customized ERP system can fail if employees are unwilling or unable to use it. The key to success is user acceptance, which begins at the design stage. It is important to involve key users from all departments—such as finance, logistics, HR, and sales—in the process. This ensures that the system meets actual operational needs. Resistance often stems from employees not understanding the purpose and benefits of the change. Therefore, not only technical training is needed, but also comprehensive change management. Clear communication and the role of "change champions" can help build trust.
As PROGEN experts put it:
"ERP selection is not an 'IT project', but a strategic decision that determines the long-term operation of the company." – PROGEN
User acceptance testing (UAT) is also a critical step. This phase gives employees the opportunity to test the system with real data and business scenarios before it goes live. This not only tests the functionality of the system, but also increases user confidence. It is interesting to note that companies that involved external consultants in the implementation achieved an 85% success rate.
It is important that implementation does not end with a sharp start. A dedicated support team must continuously monitor user feedback, identify opportunities for improvement, and address any issues that arise.
Business process reengineering (BPR) is also essential during implementation. This prevents us from simply automating old, ineffective work processes. Setting specific, measurable goals—such as "reducing closing time from 10 days to 5 days"—can help employees see the tangible benefits of the new system. In addition to such goals, demos based on specific business scenarios can also effectively illustrate how the system can help with everyday work.
All of these elements contribute to a successful ERP implementation, ensuring a smooth transition and immediate business benefits.
ERP evaluation comparison table
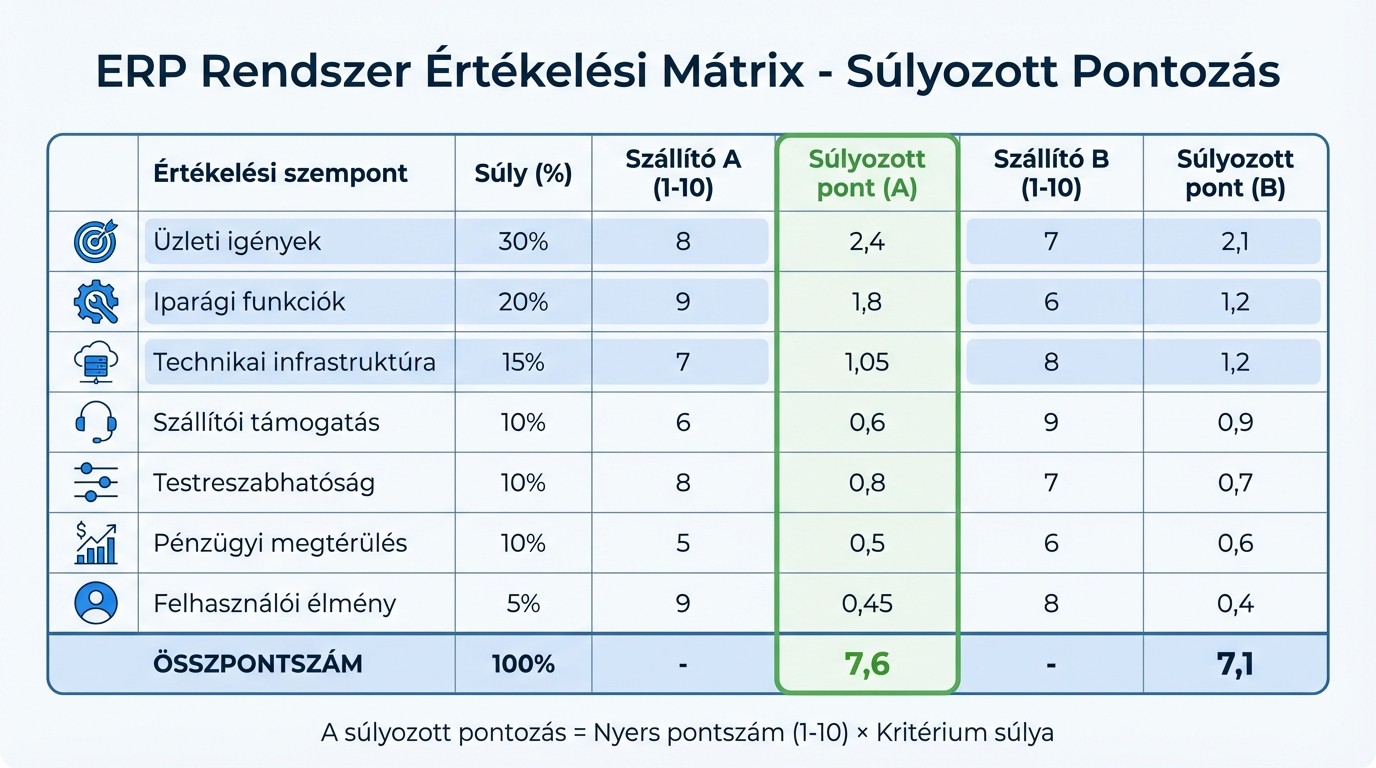
Weighted evaluation table for ERP system selection criteria
The table below provides an objective and weighted comparison for evaluating ERP systems based on seven key criteria. The aim of this method is to provide a more accurate picture of supplier performance by eliminating subjective opinions. Each criterion is assigned a weight that reflects its importance, and supplier performance is scored accordingly.
The criteria are divided into three categories: "Very important" (3 points), "Important" (2 points), and "Less important" (1 point). For example, if industry-specific features are of paramount importance, they are given a higher weighting. The weighted score is calculated by multiplying the supplier's raw score (on a scale of 1–10) by the weight of the criterion and then adding the results together. The table below shows the detailed evaluation.
Evaluation criteria | Weight (%) | Supplier A (1-10) | Weighted point | Supplier B (1-10) | Weighted point |
Business needs | 30% | 8 | 2,4 | 7 | 2,1 |
Industry functions | 20% | 9 | 1,8 | 6 | 1,2 |
Technical infrastructure | 15% | 7 | 1,05 | 8 | 1,2 |
Supplier support | 10% | 6 | 0,6 | 9 | 0,9 |
Customizability | 10% | 8 | 0,8 | 7 | 0,7 |
Financial return | 10% | 5 | 0,5 | 6 | 0,6 |
User experience | 5% | 9 | 0,45 | 8 | 0,4 |
Total score | 100% | 7,6 | 7,1 |
To ensure that the scoring reflects the needs of the entire company, it is worth involving representatives from all relevant departments —from senior management to end users. This will ensure that the results enjoy broad acceptance.
Professional consultants often use the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) method, in which criteria are compared in pairs on a scale of 1 to 9. This helps to assign mathematically sound weights to the criteria. It is also important to check the consistency ratio (CR) to ensure that the weights assigned by different team members do not conflict with each other.
The evaluation model therefore provides a transparent and structured framework for comparing ERP solutions, which can help you make the best decision.
Conclusion
Choosing an ERP system is much more than simply purchasing software—it is a strategic decision that can determine how your company operates and competes for the next seven years. The seven evaluation criteria—from defining business needs to user experience—help ensure that the system you choose is truly aligned with your organization's goals.
A structured selection process can significantly reduce the chances of implementation failure. As KPMG points out, "the key to successful system implementation is effective and thorough advance planning. " Tools such as weighted scoring systems, the involvement of different departments, and the review of business processes all contribute to objective and well-founded decision-making.
At the same time, it is crucial to take future needs into account in order to avoid costly re-launches. If a system is chosen with too narrow a focus, it may be necessary to introduce a new one within a few years, which could cost three or four times more than the original investment.
It is important to involve the relevant departments early on in the process, prepare a weighted evaluation table, and thoroughly examine the long-term support options offered by suppliers. Currently, only 4% of small and medium-sized enterprises in Hungary use ERP systems, compared to an EU average of 34%. This offers a huge opportunity for those who now want to take steps towards digital transformation.
A well-chosen ERP system not only provides a competitive advantage, but also lays the foundation for digital transformation. Start your structured evaluation today and make the decision that will support your company's growth in the long term!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why choose an industry-specific ERP system?
Industry-specific ERP systems offer solutions tailored specifically to the needs of a given sector, helping businesses operate more efficiently. These systems include features that are precisely aligned with the regulatory framework, workflows, and data management requirements of the industry.
One of the biggest advantages of such systems is that they can significantly reduce administrative burdens while automating processes. This not only saves time, but also ensures data reliability and accuracy. With integrated data, companies can make decisions faster, perform more accurate analyses, and operate more efficiently.
In addition, industry-specific ERP systems greatly contribute to regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and traceability. These factors not only increase competitiveness but also improve customer satisfaction, as companies can meet their customers' needs more accurately and quickly.
These systems therefore enable businesses to operate in a manner tailored to the specific characteristics of their industry, thereby achieving their business objectives more effectively.
What role does technical infrastructure play in the success of an ERP system?
One of the cornerstones of successful ERP system operation is the right technical infrastructure. A stable, state-of-the-art back-end system ensures that ERP supports the company's daily operations quickly, reliably, and securely. This means not only data security and continuous availability, but also minimized downtime, both of which directly contribute to cost reduction and improved operational efficiency.
Another advantage of a well-designed infrastructure is the scalability of the system. This allows the company to easily manage growth or respond to new business needs. That is why it is crucial that the technical background not only meets current needs, but also fits the company's strategy in the long term. This ensures competitiveness and continuous development in an ever-changing market environment.
What factors should be considered when selecting an ERP supplier?
When selecting an ERP supplier, one of the most important goals is to find a partner who not only understands your current needs, but also offers reliable and stable solutions in the long term. The primary considerations are the supplier's experience and thorough knowledge of the specific characteristics of the industry. This ensures that the system will run smoothly and that the necessary support will always be available.
It is important to carefully examine the features offered by the supplier, the integration options, and the scalability of the system. A well-scalable ERP system can keep pace with the growth of the company and constantly changing business needs. When planning costs, it is important to consider not only the price, but also how many users are needed, what modules need to be implemented, and what customization options are available. Careful consideration of these factors will help you avoid unexpected expenses later on.
In addition, special attention should be paid to the support and maintenance services provided by the supplier, the manageability of the system, and compliance with local regulations. These factors ensure that the system not only operates efficiently on a daily basis, but also meets the company's expectations and legal requirements in the long term. A well-chosen ERP supplier therefore represents significant value not only from a technological perspective, but also from a business perspective.

